Art-labeling activity structure of compact bone is a topic of significant interest in the field of bone biology, providing insights into the intricate organization and function of this vital tissue. This article delves into the histological labeling techniques, morphological features, structural hierarchy, mechanical properties, and clinical significance of compact bone, offering a comprehensive understanding of its architecture and function.
Histological Labeling of Compact Bone: Art-labeling Activity Structure Of Compact Bone
Histological labeling techniques are essential for visualizing and understanding the intricate structure of compact bone. These techniques involve staining bone tissue with specific dyes or reagents that selectively bind to different components, allowing researchers to identify and study specific features.
One of the most widely used histological staining techniques for compact bone is hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. H&E stains the nuclei of cells blue and the cytoplasm pink, providing a basic overview of the bone’s cellular structure. Other stains, such as Masson’s trichrome, can differentiate between collagen fibers and mineralized bone matrix, highlighting the organization of the tissue.
Morphological Features of Compact Bone, Art-labeling activity structure of compact bone
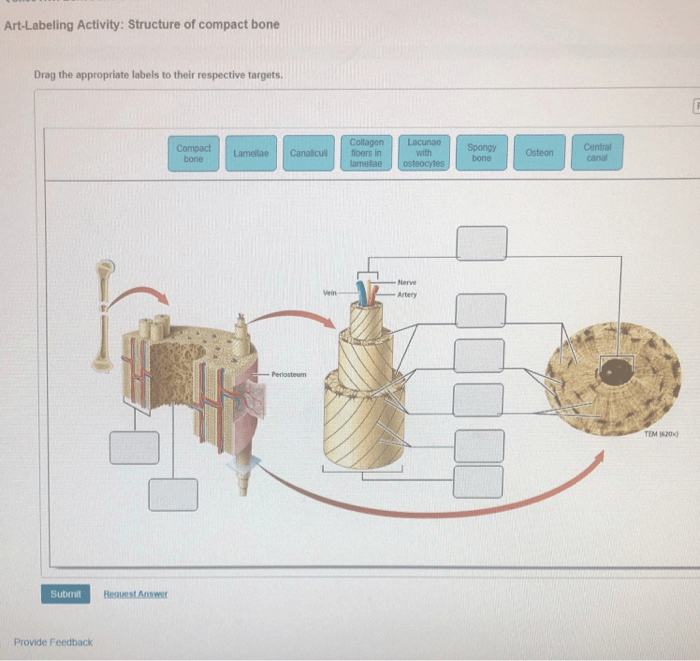
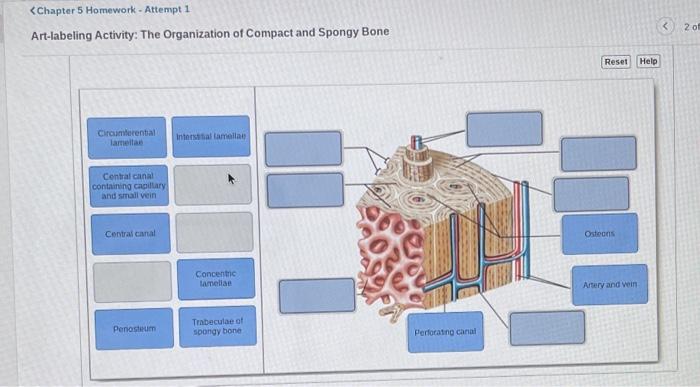
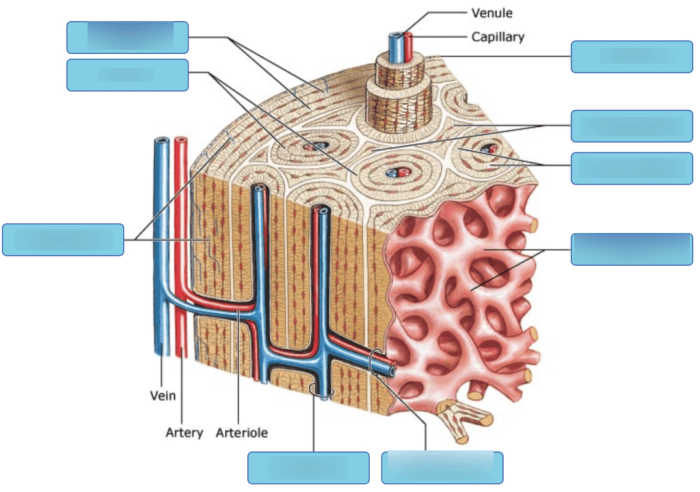
Compact bone is characterized by its dense, highly organized structure. The basic unit of compact bone is the osteon, a cylindrical structure consisting of concentric lamellae of mineralized bone matrix surrounding a central Haversian canal.
Within the osteons, osteocytes reside in small cavities called lacunae. Canaliculi, tiny channels radiating from the lacunae, connect the osteocytes to each other and to the Haversian canal, allowing for nutrient and waste exchange.
Structural Hierarchy of Compact Bone
Compact bone exhibits a hierarchical organization, ranging from the nanoscale to the macroscale. At the nanoscale, bone is composed of collagen fibers and hydroxyapatite crystals. These components are arranged in a highly ordered manner to form the lamellae and osteons.
At the microscale, the osteons are organized into larger units called haversian systems. Haversian systems are surrounded by interstitial lamellae, which are remnants of older osteons that have been remodeled.
At the macroscale, compact bone forms the outer layer of long bones and the dense inner core of flat bones. It provides structural support and protection for the body.
Mechanical Properties of Compact Bone
Compact bone is known for its exceptional mechanical properties, including strength, stiffness, and toughness. These properties are attributed to the unique arrangement of its structural components.
The collagen fibers provide tensile strength, while the hydroxyapatite crystals provide compressive strength. The interlocking lamellae and osteons distribute forces evenly throughout the bone, increasing its resistance to bending and twisting.
Clinical Significance of Compact Bone Labeling
Histological labeling of compact bone plays a crucial role in diagnosing and treating bone diseases. Bone biopsies can be stained with specific dyes to identify abnormalities in bone structure and composition.
For example, in osteoporosis, a condition characterized by decreased bone density, histological labeling can reveal reduced osteon density and increased porosity. This information can guide treatment decisions and monitor disease progression.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the purpose of art-labeling in compact bone?
Art-labeling techniques allow researchers and clinicians to visualize and study the intricate structure of compact bone, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of bone diseases.
How does the structural hierarchy of compact bone contribute to its function?
The hierarchical organization of compact bone, from nanoscale to macroscale, provides a unique combination of strength, stiffness, and toughness, enabling it to withstand various mechanical loads.
What are the clinical applications of compact bone labeling?
Compact bone labeling is used in bone biopsies and other diagnostic procedures to assess bone health, identify bone diseases, and guide treatment decisions.