Hesi case study traumatic brain injury – The HESI case study on traumatic brain injury embarks on an intricate journey, delving into the intricacies of a challenging medical condition. This case study serves as a valuable tool for healthcare professionals, providing insights into the assessment, intervention, and monitoring of TBI patients.
The case study presents a comprehensive overview of the patient’s condition, exploring the initial assessment, evaluation methods, and the rationale behind nursing interventions. It emphasizes the importance of monitoring progress, evaluating outcomes, and considering ethical considerations in patient care.
HESI Case Study Overview
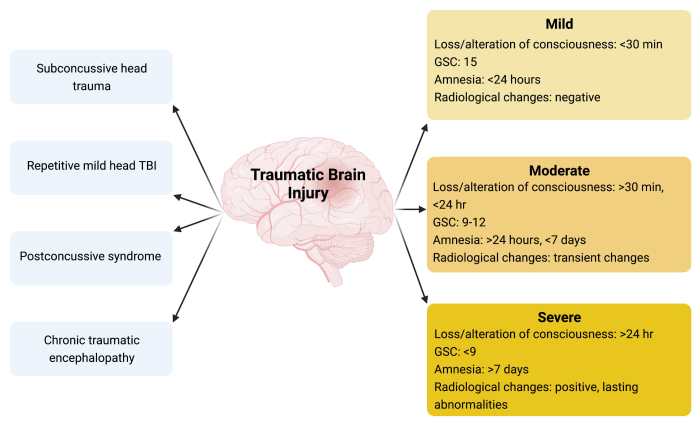
The HESI case study is a comprehensive assessment tool designed to evaluate a nurse’s ability to manage a patient with a traumatic brain injury (TBI). The case study presents a detailed account of the patient’s history, physical examination, and medical interventions.
Nurses must analyze the case study and demonstrate their understanding of TBI assessment, evaluation, and management.
Assessment and Evaluation, Hesi case study traumatic brain injury
The initial assessment of a patient with TBI involves a thorough history and physical examination. The history should include information about the mechanism of injury, loss of consciousness, and post-traumatic symptoms. The physical examination should focus on assessing the patient’s neurological status, including their level of consciousness, pupillary response, and motor function.The
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a widely used tool for assessing the severity of TBI. The GCS measures the patient’s level of consciousness, verbal response, and motor response. A score of 15 indicates a normal neurological examination, while a score of 3 indicates a deep coma.
Nursing Interventions
Nursing interventions for patients with TBI are aimed at preventing secondary brain injury and promoting recovery. These interventions include:
- Maintaining a patent airway and adequate ventilation
- Controlling intracranial pressure
- Preventing infection
- Providing nutritional support
- Managing pain
Monitoring and Evaluation
Patients with TBI require close monitoring to assess their progress and identify any complications. Monitoring parameters include:
- Neurological status
- Vital signs
- Intracranial pressure
- Electrolytes
- Blood glucose
FAQ: Hesi Case Study Traumatic Brain Injury
What is the purpose of the HESI case study on traumatic brain injury?
The HESI case study aims to provide healthcare professionals with a comprehensive understanding of the assessment, intervention, monitoring, and ethical considerations involved in the care of patients with traumatic brain injury.
What methods are used to evaluate the severity of a traumatic brain injury?
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is commonly used to assess the severity of traumatic brain injury, evaluating eye opening, verbal response, and motor response.
What are some common nursing interventions for patients with traumatic brain injury?
Nursing interventions for TBI patients may include maintaining airway patency, monitoring vital signs, administering medications, and providing emotional support.